Definitely Delegate Maybe
- Details
Simon Ricketts looks at what the future holds for the modus operandi of planning committees.
“Modernising planning committees” is one of the promised objectives of the Planning and Infrastructure Bill, likely to be introduced into Parliament this Autumn.
The Government has not yet provided any colour as to what modernisation means in this context but the general assumption is that it is likely to include moving to a national scheme of delegation, setting out which categories of planning applications should not be determined by planning committee but should instead be taken by planning officers by way of delegated powers.
Appropriate use of delegation is a good thing. Indeed, that is already reflected in the Government’s Planning Practice Guidance, unchanged for the last ten years: See “Who in a local planning authority makes a planning decision?
Section 101 of the Local Government Act 1972 allows the local planning authority to arrange for the discharge any of its functions by a committee, sub-committee, or an officer or by any other local authority. An exception where this power may not apply is where the local authority’s own application for development could give rise to a conflict of interest, when regulation 10 of the Town and Country Planning General Regulations 1992 applies.
The exercise of the power to delegate planning functions is generally a matter for individual local planning authorities, having regard to practical considerations including the need for efficient decision-taking and local transparency. It is in the public interest for the local planning authority to have effective delegation arrangements in place to ensure that decisions on planning applications that raise no significant planning issues are made quickly and that resources are appropriately concentrated on the applications of greatest significance to the local area.
Local planning authority delegation arrangements may include conditions or limitations as to the extent of the delegation, or the circumstances in which it may be exercised.
Paragraph: 015 Reference ID: 21b-015-20140306
Revision date: 06 03 2014”
The Local Government Association has published this piece which sets out examples of categories of applications included in individual authorities’ schemes of delegation as requiring determination by committee – together with a brief analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of including each category. As we know, almost every authority has a slightly different set of rules – and sometimes it takes some website burrowing (a particular curse upon every authority which does not a clear index to its constitution) to ascertain what they are…
However, despite what it may seem like to practitioners focused on larger applications, nearly all planning applications are of course already delegated to officers. This is a list of the authorities which last year delegated the lowest proportion of decisions to officers:
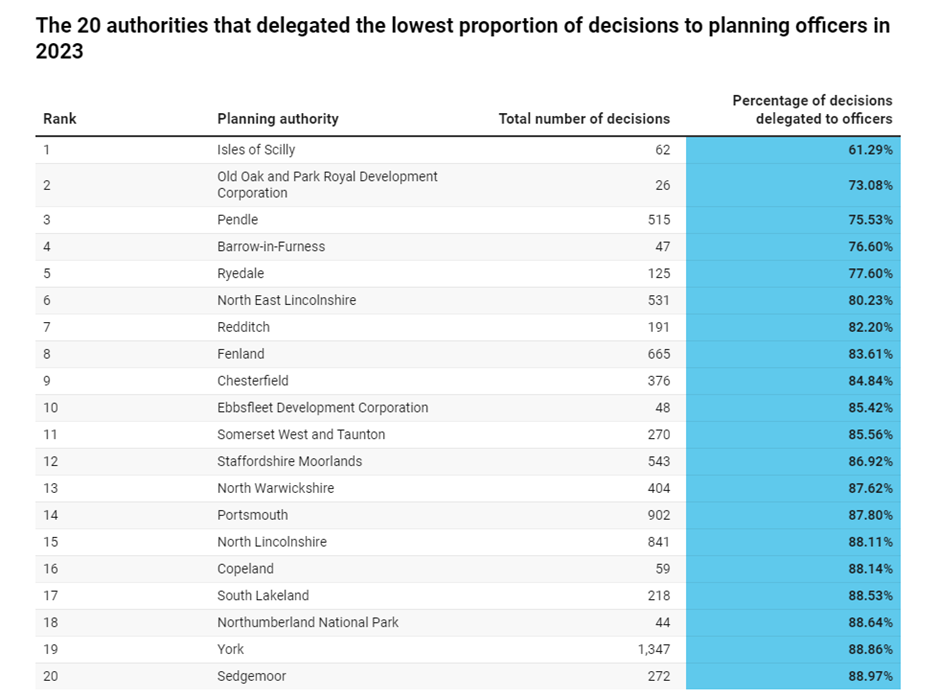
The top twenty are all 98.5% plus!
And yet still there is the sense that even more applications could be determined by officers. For instance, the RTPI published this press statement on the day of the King’s Speech (17 July 2024):
“The Institute believes planning committees need modernisation and could include a national scheme of delegation, allowing planning officers to make some decisions themselves. Qualified planners should be able to implement agreed planning policy, freeing up councillors’ time to focus on the most challenging planning cases. This change would help to unblock many applications and speed up the planning process.”
Definitely, in a more perfect system, with clear policies in an up-to-date local plan, surely applications for planning permission which accorded with the local plan should be able to be approved by officers without reference to committee, and those not in accordance refused. Local democracy should be focused on the plan rather than its implementation.
The previous Government’s 2022 Planning For The Future white paper of course took this to the max, envisaging allocations which had the effect of granting the equivalent of outline planning permission and that thereafter “the delegation of detailed planning decisions to planning officers where the principle of development has been established, as detailed matters for consideration should be principally a matter for professional planning judgement”.
Maybe indeed, we should be heading in that direction (although it is all of course predicated on having that clear, up-to-date, plan!). Is legislation required to achieve greater delegation of decision making? I’m not sure. I shall be interested to see the “one size fits all” outcome. And as with any suggested legislative change, have we looked at whether behaviour can be changed without resorting to the law? By all means come up with a scheme of delegation template – but why not then include it immediately in Planning Practice Guidance and advise authorities that they adopt it? That could make a difference by as early as next year. Legislation won’t.
In the meantime, two of the many things which keep planning lawyers busy are (1) the behaviour at meetings of planning committee members and (2) the interpretation of local authority constitutions as to how committee meetings should be run. Two recent cases of interest:
R (Greenfields (IOW) Limited v Isle of Wight Council (HH Judge Karman KC, 23 August 2024)
Read about the agony of prolonged debate of a contentious application at a committee meeting, allegations of predetermination and bullying and a councillor changing their mind at the last moment…R (Spitalfields Historic Building Trust) v London Borough of Tower Hamlets (Court of Appeal, 28 July 2024)
More agony, with successive planning committee meetings in relation to another contentious application and arguments as to which members could participate. The Court of Appeal (and before that the High Court) determined that was lawful for a local authority’s constitution to restrict voting by members on a deferred application for planning permission to those who had been present at the meeting(s) at which the application had previously been considered. However, the Supreme Court heard the subsequent appeal on 25 July 2024 and we await its final ruling.
Simon Ricketts is a partner at Town Legal. This article first appeared on his Simonicity planning law blog.
Sponsored articles
Walker Morris supports Tower Hamlets Council in first known Remediation Contribution Order application issued by local authority
Unlocking legal talent
Solicitor - Contracts and Procurement
Legal Director - Government and Public Sector
Commercial Lawyer
Locums
Poll